A wound is an injury that causes harm to the body. It is a general term for the injury produced by accidents, collisions, hits, firearms, and other factors. Yearly, millions of people in the United States damage themselves. These injuries range from minor to severe. Injuries may occur at work or at play, inside or outside, while driving or strolling across the street. Additionally, wounds are injuries that break the skin or other bodily tissues. Cuts, scrapes, scratches, and pierced tissue are examples. Wounds are occasionally caused by accident but are also frequently caused by surgery, sutures, and stitches. A small wound is typically not dangerous, but it must be cleaned and cared for. Severe and infected wounds may necessitate immediate first-aid treatment, followed by a trip to the doctor. You should also seek Bakersfield wound care if:
- You cannot close it on yourself.
- The wound is severe or profound.
- It doesn’t heal.
- You cannot cease the bleeding or remove the dirt.
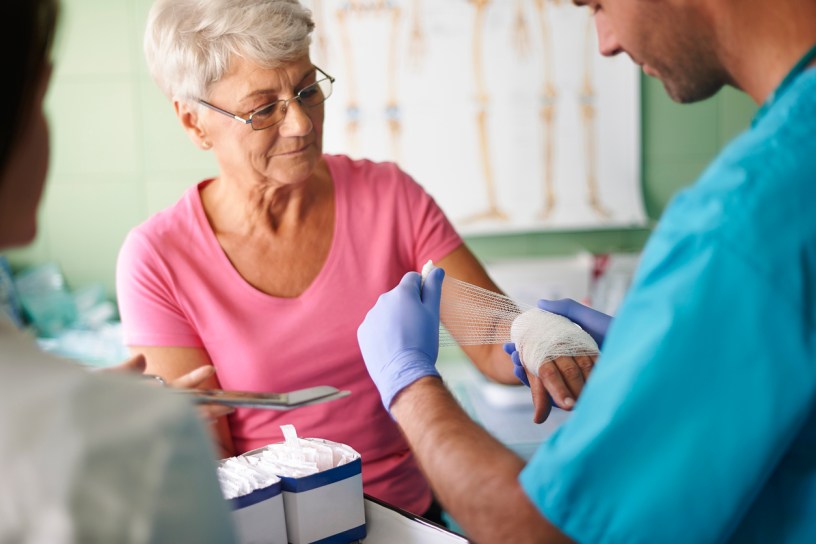
How to treat surgical wounds
A surgical wound is a cut or incision made through the skin during an operation, generally using a knife. A surgical wound can also be caused by a drain used during surgery. The size of surgical wounds varies greatly. Sutures are typically used to seal them; however, they are sometimes left open to heal. Treatment for a surgical wound is frequently determined by its location in the body. Surgical dressings will be applied to the wound by doctors. And you must change it regularly. The skin around the surgical area will almost certainly need to be washed, usually with saltwater and soap. You may even be required to rinse the wound with saltwater. Furthermore, filling the syringe with saltwater and spraying the area around the incision is part of the procedure.
Common wound complications
- Infections: Pus leakage, foul odor, fever, dull throbbing pain, minor edema, and heat at the wound site are all symptoms of wound infection.
- Scarring: Regenerated cells have unique properties and fibrous tissue that can cure the wound but may create a scar.
- Inflammation: Inflamed wounds are hot, red, painful, swollen, and difficult to move.
- Loss of function: Many wounds can be crippling and even fatal if a major organ, blood artery, or nerve is destroyed. In either case, the injured limb or region will lose functioning while the incision is still new or healing until all lost or damaged tissue is healed.
How to prevent wounds
The best strategy to avoid all forms of wounds is to practice optimal safety precautions, paying particular attention to surrounding risks in new surroundings. Always take precautions when handling sharp, corrosive, or heated materials.
It is critical to respond quickly if you have a slight or severe wound. You can treat some wounds at home, but this is not always the case. You should seek medical aid if you have a deep cut or a lot of bleeding. It guarantees that you receive the best possible care and lowers your risk of injury and illness. Call Heart Vascular and Leg Center to schedule your consultation today to determine which wound care technique is best for you.